Respiratory diseases are connected with the outside world, which makes the outside organic or inorganic dust, various microorganisms, protein allergens, and harmful gases inhale into the lungs, causing a variety of respiratory diseases. The incidence rate of respiratory diseases, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), bronchial asthma, and pulmonary interstitial fibrosis are increasing significantly due to smoking, air pollution, inhalation of various physical, chemical and biological factors, and aging of the population.
Acute lung injury model
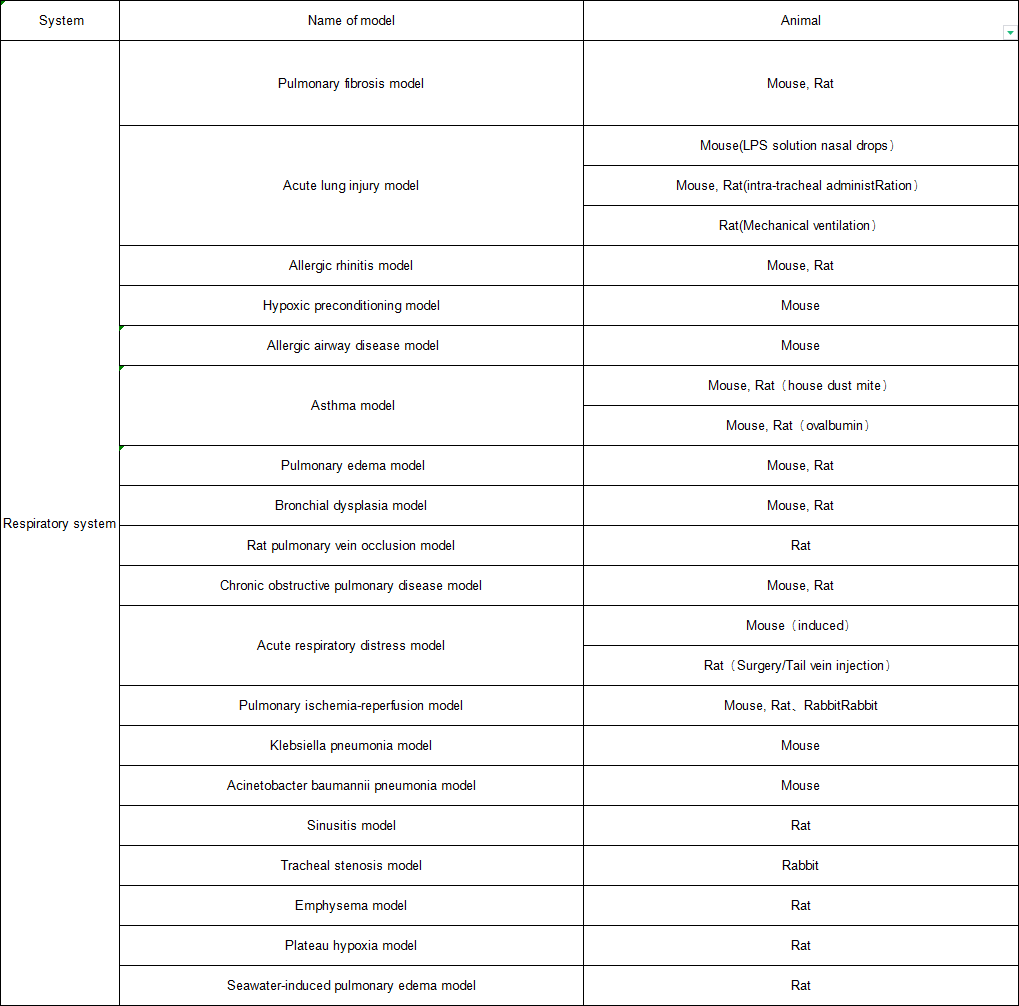
Establishment of acute lung injury model by endotracheal instillation of LPS
(Control Group)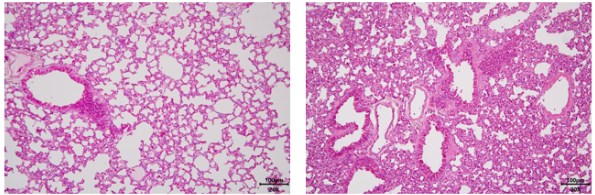 (Model Group)
(Model Group)
Fig. 1 Acute lung injury model. HE staining pictures of lung tissue showed that the pulmonary septum in the model group was significantly thickened, and inflammatory cell infiltration was obvious.
Asthma model
Mouse asthma model induced by house dust mite
Asthma model induced by ovalbumin in rats
Asthma model of mice induced by Ascaris lumbricoides protein
(Control Group)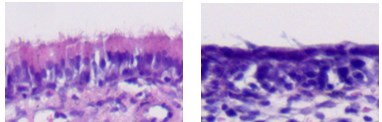 (Model Group)
(Model Group)
Fig. 3 Rat model of sinusitis. The HE staining results of nasal mucosa showed that the cilia of the model group disappeared, the nasal mucosa structure was disordered, the submucosal tissue was accompanied with edema and bleeding symptoms, and there were a large number of inflammatory cells infiltration.
Rabbit model of tracheal stenosis
Establishment of rabbit tracheal stenosis model by injury of tracheal intima with hair brush
Sepsis lung injury model
Establishment of sepsis lung injury model in mice by cecal ligation
Hypoxia model of rats at high altitude
Low-pressure oxygen chamber simulates air pressure and oxygen concentration at 5000m above sea level to establish plateau hypoxia model