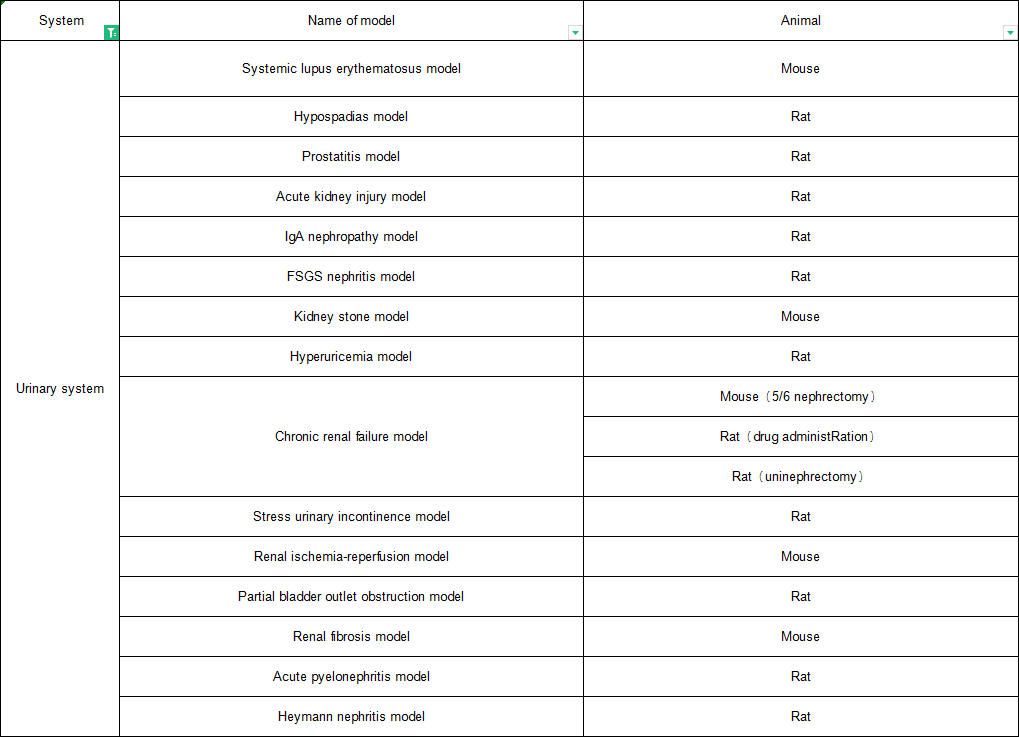
Urinary system diseases refer to the primary and secondary diseases of kidney, ureter, bladder, urethra and its accessory glands. Data shows that the incidence rate of adult chronic kidney disease is as high as 10%, which has become a hidden killer of human health. The most common reason is immune and metabolic disorders. The primary causes of these chronic kidney diseases are very complex, including various primary and secondary kidney diseases. To understand the pathogenesis and prevention measures of different kidney diseases, it is necessary to have corresponding experimental animal models.
Systemic lupus erythematosus model
MRL-lpr mice (spontaneous symptoms at 16 weeks of age)
Renal fibrosis model
Establishment of renal fibrosis model in mice by unilateral ureteral ligation
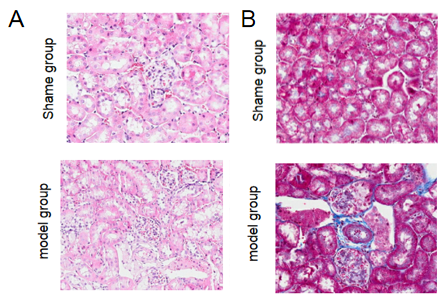
IgA nephropathy model
Establishment of mouse IgA nephropathy model by intraperitoneal injection of IgA protein
Hyperuricemia model
Establishment of hyperuricemia model in rats fed with 25% yeast extract feed combined with intraperitoneal injection of potassium oxyzinate
Acute pyelonephritis model
Establishment of acute pyelonephritis model in rats by unilateral ureteral ligation and intravesical injection of Escherichia coli
Acute renal injury model
Acute renal injury induced by intraperitoneal injection of aristolochic acid A in rats
(Control Group)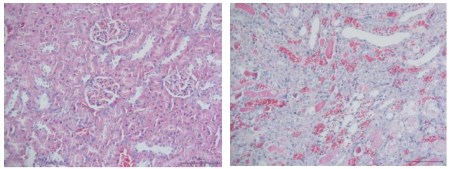 (Model Group)
(Model Group)
Fig. 2 Acute renal injury model. HE staining of renal tissue showed that the glomerulus showed enlarged pathological changes, tissue type and protein type appeared in the tubules, and the epithelial cells of renal tubules fell off and acute tubular necrosis occurred
Heymann nephritis
Heymann nephritis induced by Fraction 1A (Fx1A) antigen in rats
Uric acid nephropathy model
Rat uric acid nephropathy model induced by intragastric administration of potassium oxyzinate and uric acid
(Control Group)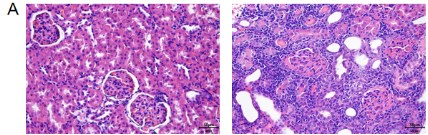 (Model Group)
(Model Group)
A=Control Group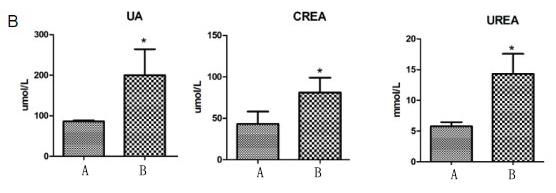 B=Model Group
B=Model Group
Fig. 3 Model of uric acid nephropathy. Figure A HE staining showed that a large number of inflammatory cells infiltrated the renal interstitium, renal tubules expanded, and glomerular mesangium thickened in the model group. Figure 2 Biochemical results showed that the content of serum uric acid UA and serum uric acid UA in the model group increased significantly.