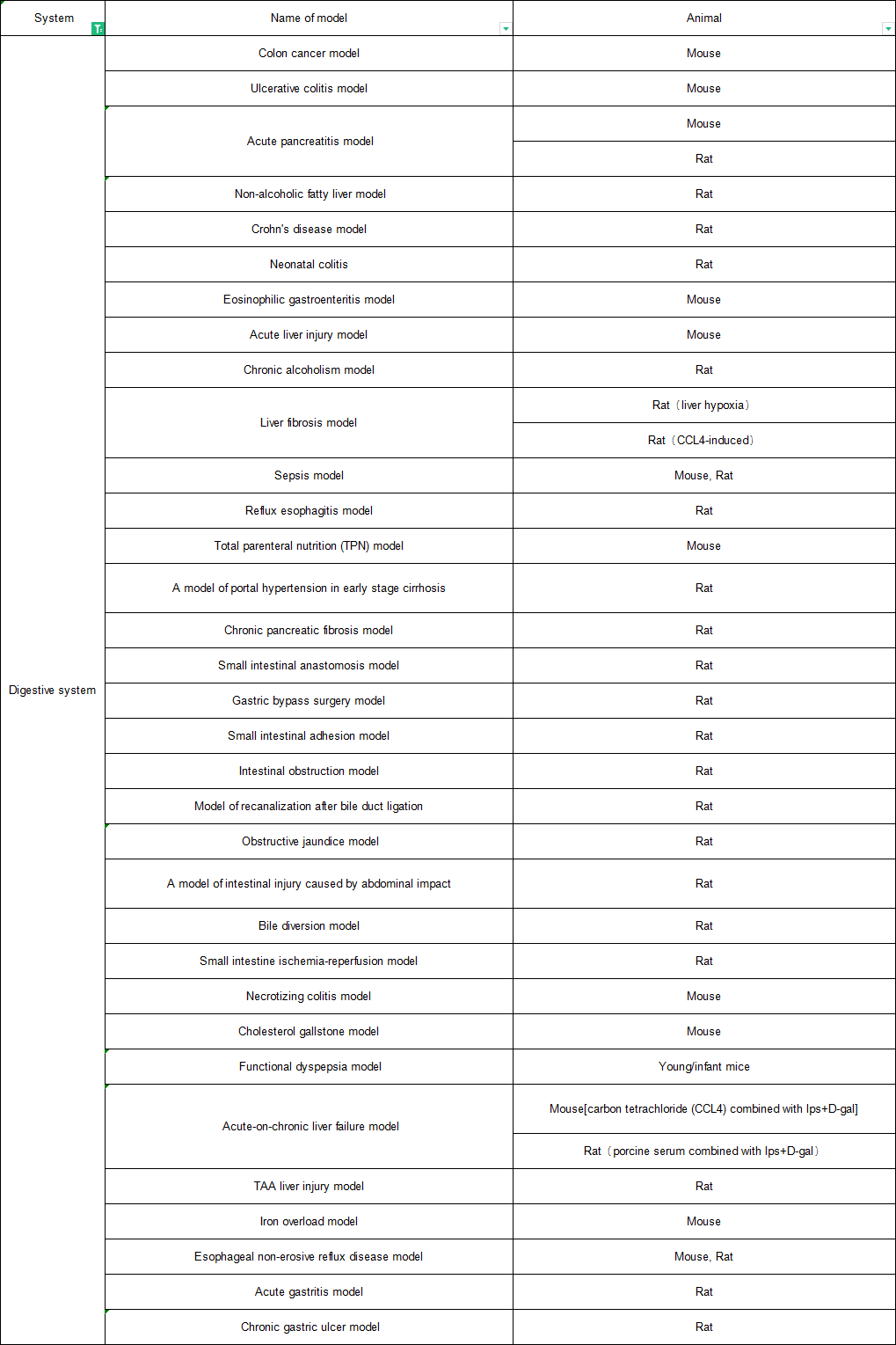
The digestive system is composed of digestive tract and digestive gland. Digestive system diseases include upper and lower digestive tract diseases such as esophagus, stomach, small intestine (duodenum, jejunum, ileum), large intestine (caecum, colon, rectum, anal canal), and various diseases of small digestive glands, hepatopancreas and other large digestive glands scattered in the wall of digestive tract. In the research process of digestive system diseases, establishing various animal models of digestive tract that meet the research needs is an important tool and level for exploring the occurrence, development and prognosis of diseases.
Colon cancer model
Mouse colon cancer model induced by AOM intraperitoneal injection combined with DSS
Ulcerative colitis model
DSS drinking water induced ulcerative colitis in mice
(control group)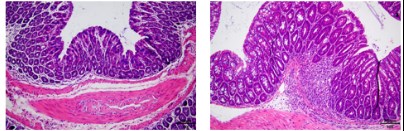 (Model Group)
(Model Group)
Figure 1 Ulcerative colitis. HE staining results showed that the intestinal mucosa of the model group was significantly damaged, and a large number of inflammatory cells infiltrated in the submucosa.
acute pancreatitis
Establishment of acute pancreatitis model in rats by retrograde injection of sodium taurocholate into pancreatic islet
Rat model of acute pancreatitis induced by intraperitoneal injection of hydatin and LPS
(control group)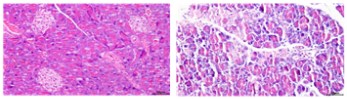 (Model Group)
(Model Group)
Nonalcoholic fatty liver model
Rat model of nonalcoholic fatty liver induced by high-fat diet combined with carbon tetrachloride
Liver injury model
LPS combined with galactose induced liver injury in mice
Hepatic fibrosis model
Hepatic hypoxia induced by ligation of the proper hepatic artery leads to hepatic fibrosis in rats
Chronic alcoholism model
Chronic alcoholism model induced by alcohol gavage
Reflux esophagitis model
Rat model of reflux esophagitis induced by esophagoduodenal anastomosis
TPN model
Establishment of parenteral nutrition model in mice by injecting nutrient solution into jugular vein with microinjection pump
Portal hypertension model of early cirrhosis
Establishment of portal hypertension model of early cirrhosis by ligation of common bile duct
(control group)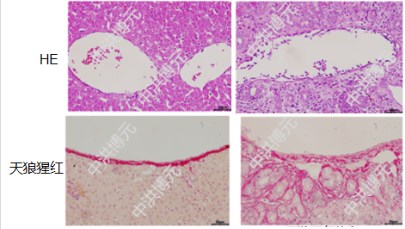 (Model Group)
(Model Group)
Fig. 3 Portal hypertension model of early cirrhosis. HE and Sirius red staining showed that,
Chronic pancreatic fibrosis model
Establishment of chronic pancreatic fibrosis model in rats by retrograde injection of trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid into bile duct
Model of recanalization of biliary obstruction
A rat model of bile duct obstruction and recanalization was established after ligation of common bile duct for one week
Small intestine ischemia reperfusion model
Establishment of small intestinal ischemia reperfusion model in rats by occlusion and reperfusion of small intestinal artery
Crohn's enteritis
Establishment of Crohn's enteritis model in rats by intracolon injection of DNCB-ethanol solution
Eosinophilic gastroenteritis model
Mouse eosinophilic gastroenteritis model induced by ovalbumin
Chronic plus acute liver failure
Establishment of chronic and acute liver failure in rats by lipopolysaccharide combined with D-galactose
Nonerosive gastroesophageal reflux disease model
Establishment of non-erosive gastroesophageal reflux model in rats by intraperitoneal injection of OVA and esophageal drip of hydrochloric acid
Functional dyspepsia model
Functional dyspepsia model induced by iodoacetamide in rats
Chronic gastric ulcer model
A rat model of chronic gastric ulcer induced by glacial acetic acid
(control group)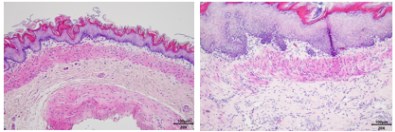 (Model Group)
(Model Group)
Fig. 4 Chronic gastric ulcer model. The HE results showed that the model group had severe mucosal damage, structural destruction and a large number of inflammatory cells infiltration.
Iron overload model
Iron overload model in mice induced by intraperitoneal injection of iron dextran

 (Model Group)
(Model Group)
 (Model Group)
(Model Group)
 (Model Group)
(Model Group)
 (Model Group)
(Model Group)
