
Tumor cells and cancer cells
Tumor cells can be divided into benign and malignant cells; cancer cells are malignant, which are cells that can spread. Tumor cells include cancer cells, and their common feature is cells that are out of control at the genetic level and can proliferate indefinitely. Cancer cells have three significant basic characteristics: immortality, migration, and loss of contact inhibition.
Commonly used tumor-forming cells in the laboratory
Conventional cells that are prone to tumor formation: Hep-G2 (liver cancer), Hep2 (larynx cancer), NCI-H460 (large cell lung cancer), A431 (epidermal cancer), SK-OV-3 (ovarian cancer), MCF-7 ( Breast cancer) SKBR3, A375/B16-F10 (human melanoma cells), SGC7901 human gastric tumor cells, KB human oral epidermoid cancer cells can form tumors but relatively slow cells: CNE (nasopharyngeal carcinoma), A549 (lung cancer) , SPC-A-1 (lung adenocarcinoma), HT-29 (colon cancer), BEL-7402 (liver cancer), MDA-MB-231 breast cancer, CT26 (mouse colon cancer cell), SH-SY5Y (human nerve Blastoma cells), U251 (human glioma cells), BGC-823 (human gastric cancer cells), PC-3 (human prostate cancer cells)
Some of the more controversial cells: Hela (cervical cancer), HCT (human ileocecal carcinoma/human colorectal cancer adenocarcinoma). Others: BMSC (Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells) recognize nude mice Athymic nude mice (Nude Mouse, referred to as nude mice). It has become an indispensable experimental animal model in the field of medical biology research. Especially in oncology, immunology, safety evaluation of drugs and biological products, and the screening of effective drugs, it has special value. Nude mice (homozygous nu/nu mutant mice) are mainly hairless (but a kind of fine-hair histology evidence of hairy follicles can be seen) and lack of normal thymus. Heterozygous mice (nn/+) behaved normally in all aspects.
There are several mutant genes in mice, which can produce a hairless phenotype, such as athymic nude mice (Nude), nude mice (Naked), hairless mice (Hairless), and no nose hair mice (Rhinol) Don’t confuse these mutant mouse genes with each other. The only characteristic of nude mice is the thymic defect phenotype. Therefore, the terms "nude mice" and "hairless mice" cannot be used interchangeably.
Nude mice: poor resistance and easy to survive in SPF environment. The cages, bedding, feed, and drinking water used are suffering from viral hepatitis and pneumonia, so the requirements for breeding and reproduction are relatively strict, and they all require strict sterilization. Sterilize and use isolators for breeding to ensure long-term survival and reproduction. Nude rats: The general characteristics are similar to nude mice, but there are still sparse coats on the trunk. They are not completely hairless like nude mice, and the head and limbs are more hairy. Naked rats are susceptible to respiratory diseases.

Nude mice

Nude rat
the choice of nude mice
Although it is said that using nude rats instead of nude mice has the advantages of large transplanted tumors, large blood volume, and some minor surgical operations. Therefore, it has certain advantages over nude mice. Its disadvantage is that the maintenance cost is higher than that of nude SPF mice. In addition, nude rats are not very popular at present. Therefore, BALB/c-nu nude mice are commonly used in our laboratory.
With the increase of the age of nude mice or the influence of related factors (such as virus infection), normal T cells in nude mice will increase. Therefore, 4--6 week-old nude mice are generally used for tumor inoculation experiments.
Tumor formation in nude mice
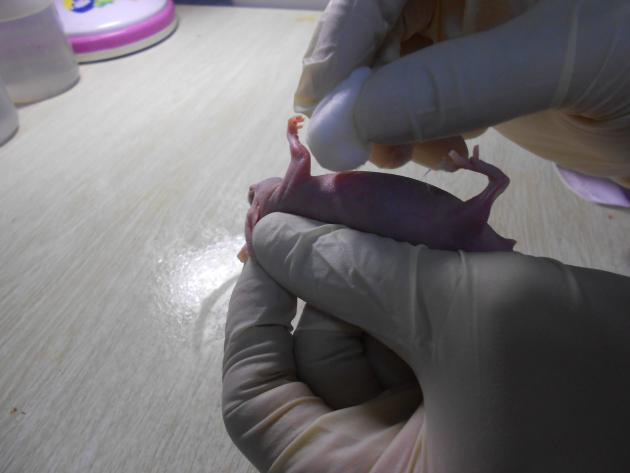
Disinfection of inoculation site
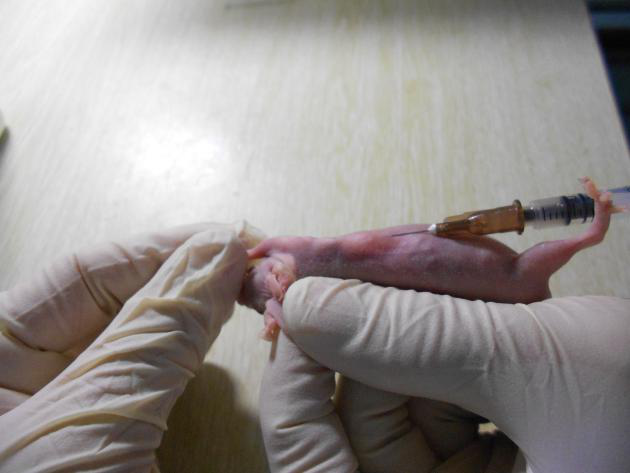
Vaccination
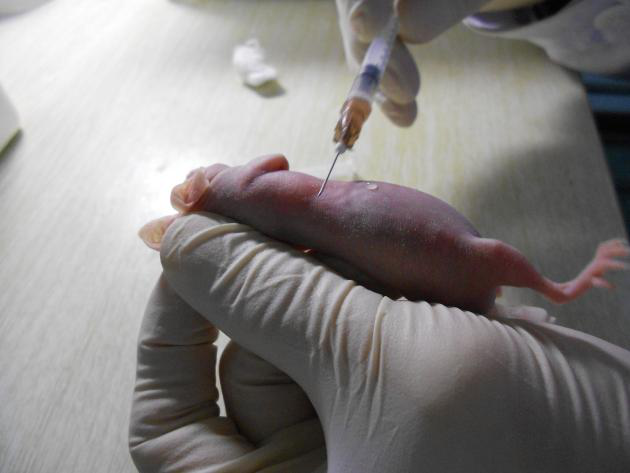
Empty the needle port
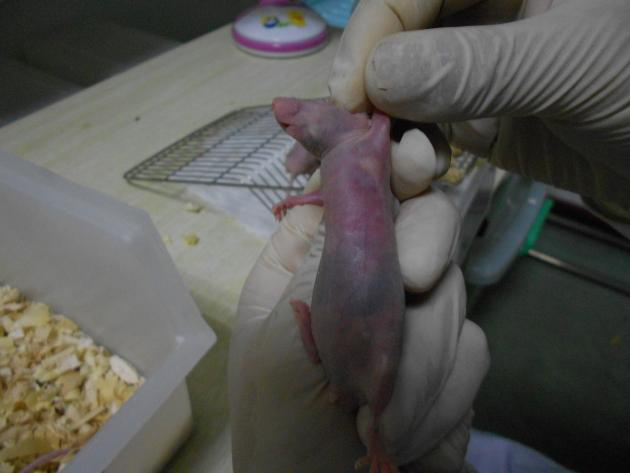
Observe after inoculation (cell cluster)
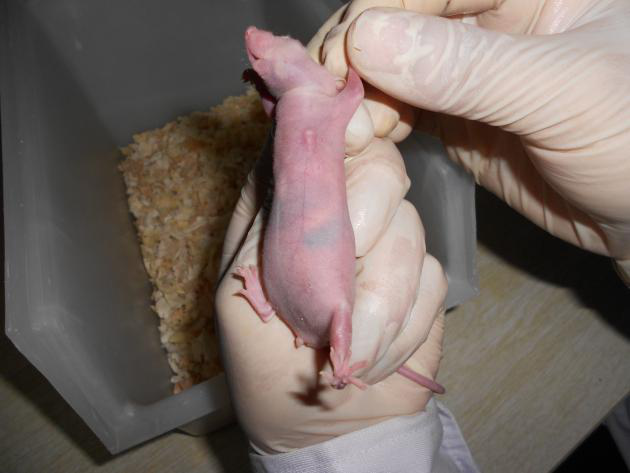
Observation after vaccination (tumor)
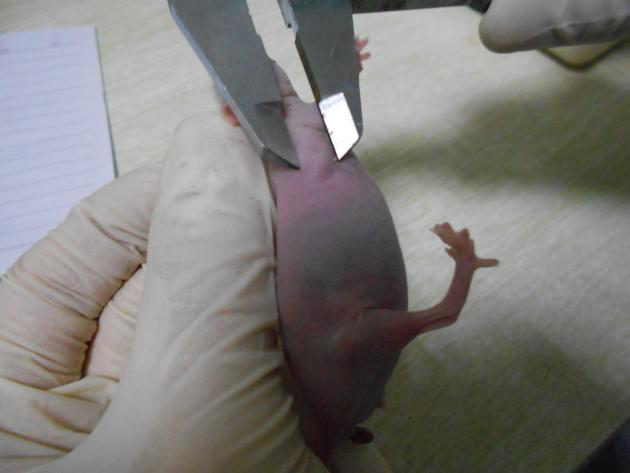
Tumor measurement
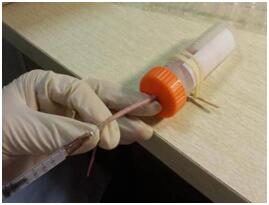
Tail vein injection
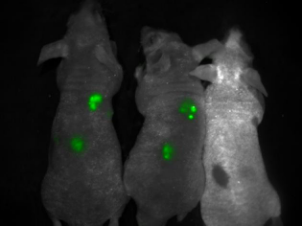
Nude mouse in vivo fluorescence
Tumor cells and cancer cells
Tumor cells can be divided into benign and malignant cells; cancer cells are malignant, which are cells that can spread. Tumor cells include cancer cells, and their common feature is cells that are out of control at the genetic level and can proliferate indefinitely. Cancer cells have three significant basic characteristics: immortality, migration, and loss of contact inhibition.
Commonly used tumor-forming cells in the laboratory
Conventional cells that are prone to tumor formation: Hep-G2 (liver cancer), Hep2 (larynx cancer), NCI-H460 (large cell lung cancer), A431 (epidermal cancer), SK-OV-3 (ovarian cancer), MCF-7 ( Breast cancer) SKBR3, A375/B16-F10 (human melanoma cells), SGC7901 human gastric tumor cells, KB human oral epidermoid cancer cells can form tumors but relatively slow cells: CNE (nasopharyngeal carcinoma), A549 (lung cancer) , SPC-A-1 (lung adenocarcinoma), HT-29 (colon cancer), BEL-7402 (liver cancer), MDA-MB-231 breast cancer, CT26 (mouse colon cancer cell), SH-SY5Y (human nerve Blastoma cells), U251 (human glioma cells), BGC-823 (human gastric cancer cells), PC-3 (human prostate cancer cells)
Some of the more controversial cells: Hela (cervical cancer), HCT (human ileocecal carcinoma/human colorectal cancer adenocarcinoma). Others: BMSC (Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells) recognize nude mice Athymic nude mice (Nude Mouse, referred to as nude mice). It has become an indispensable experimental animal model in the field of medical biology research. Especially in oncology, immunology, safety evaluation of drugs and biological products, and the screening of effective drugs, it has special value. Nude mice (homozygous nu/nu mutant mice) are mainly hairless (but a kind of fine-hair histology evidence of hairy follicles can be seen) and lack of normal thymus. Heterozygous mice (nn/+) behaved normally in all aspects.
There are several mutant genes in mice, which can produce a hairless phenotype, such as athymic nude mice (Nude), nude mice (Naked), hairless mice (Hairless), and no nose hair mice (Rhinol) Don’t confuse these mutant mouse genes with each other. The only characteristic of nude mice is the thymic defect phenotype. Therefore, the terms "nude mice" and "hairless mice" cannot be used interchangeably.
Nude mice: poor resistance and easy to survive in SPF environment. The cages, bedding, feed, and drinking water used are suffering from viral hepatitis and pneumonia, so the requirements for breeding and reproduction are relatively strict, and they all require strict sterilization. Sterilize and use isolators for breeding to ensure long-term survival and reproduction. Nude rats: The general characteristics are similar to nude mice, but there are still sparse coats on the trunk. They are not completely hairless like nude mice, and the head and limbs are more hairy. Naked rats are susceptible to respiratory diseases.
the choice of nude mice
Although it is said that using nude rats instead of nude mice has the advantages of large transplanted tumors, large blood volume, and some minor surgical operations. Therefore, it has certain advantages over nude mice. Its disadvantage is that the maintenance cost is higher than that of nude SPF mice. In addition, nude rats are not very popular at present. Therefore, BALB/c-nu nude mice are commonly used in our laboratory.
With the increase of the age of nude mice or the influence of related factors (such as virus infection), normal T cells in nude mice will increase. Therefore, 4--6 weeks old nude mice are generally used for tumor inoculation experiments.
nude mice tumor
Nude mice in vivo fluorescence
Precautions
(1) First of all, you have to determine whether your cells can form tumors, or whether the effect of tumor formation is good! Check the literature for this
(2) Cell inoculation amount is 1*107/200ul/only, or concentrated to 1*107/100ul/only, adjust the cell amount according to the tumor-forming effect of tumor cells, and the maximum shall not exceed 1*107. Tumor inoculation experiments generally use 4--6 weeks old nude mice. Too old nude mice will increase the difficulty of tumor formation and enlarge individual differences.
(3) According to personal experience, the back, underarms, and neck can be used for the vaccination site. Of course, underarms and neck have the best effect.
(4) During inoculation, the nude mouse should be injected from the side of the body slightly above the waist. Make sure that the distance from the inoculation point is less than the length of the needle, and walk toward the head. Never pierce the skin or muscle layer. Fortunately, it will be completed within 1 hour. You can put the cells in an ice box for temporary storage.
(5) After subcutaneous tumors in mice, immunosuppressive agents, such as cyclophosphamide (2mg each for two days) can be used to accelerate the growth of tumors (we haven't tried it in our laboratory).
(6) Generally one to two weeks can be observed whether the tumor is successful. After successful tumor formation, our laboratory routinely measures the tumor every other day, and finally collects the data to draw the tumor growth curve (if the customer requests it separately).
(7) Finally, don’t worry that the nude mice can’t bear it. Do bold inoculations. You must observe and record the tumor growth and the situation of the nude mice. The tumor formation is very fast, and the follow-up recording and measurement are very slow.