
Cerebrospinal fluid is a specimen often used in animal experimental research, and has irreplaceable research value in the research fields of brain injury mechanisms, biomarkers and drug therapy. However, the rat ventricles and subarachnoid space are narrow, and the internal blood vessels are abundant. The low success rate of cerebrospinal fluid collection is a technical problem faced by many researchers, because the process of extracting cerebrospinal fluid is complicated and punctures the medulla oblongata to death. By referencing the literature and improving the previously reported method of collecting cerebrospinal fluid, this study provides an accurate, convenient, fast, and blood-free method for collecting cerebrospinal fluid in rats. .. 1. Experimental materials 1. Choose 20 SD rats provided by Shanghai Experimental Animal Center as experimental animals, weighing 300-400g.
2. Experimental equipment Brain stereotaxic equipment, micro syringe (100μl), chloral hydrate, surgical equipment, refrigerated centrifuge (CT15RE).
2. Experimental methods and results (1) Experimental methods
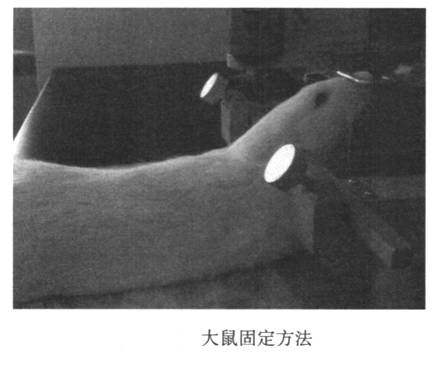
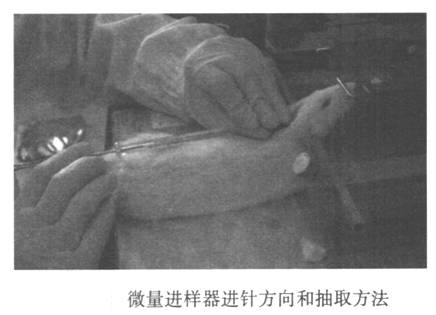
Rats were anesthetized with 7% chloral hydrate intraperitoneally. After the animal is anesthetized, insert the ear rods of the stereotactic device into the vicinity of the ears of the two ear canals, fix the ear rods to the main frame, and the ear rods on both sides have the same reading. Hook the rat’s upper incisor rod to fix the upper jaw. Raise the front tooth bar. Swing the rat's head and body to approximately 135° (Figure 24-1). Cut the rat’s headrest and sterilize it, and make a vertical incision (1.5-2 cm) along the posterior midline. Opening the skin reveals that the deltoid space behind the occiput is inverted. Use the tip of the micro syringe to push the bottom of the triangular notch and slide it along the posterior midline, and insert the needle when it reaches the large hole of the orifice. The main body is parallel. In other words, the angle between the needle and the head is about 135° (Figure 24-2). Please note that the needle advancement speed should not be too fast. When the needle tip penetrates the ligamentum flavum, there will be an obvious feeling of shedding. At this time, the needle tip enters the large water tank (0.2 mm in depth). Stop the needle. The head of the fixed needle with the left hand does not move, and the right hand slowly draws out the cerebrospinal fluid. At this time, if the withdrawal speed is slow, the blood will easily flow out, so be careful. After extraction, quickly remove the needle, transfer the cerebrospinal fluid to a 0.5 ml EP tube, centrifuge, immediately freeze with liquid nitrogen or dry ice, and then transfer it to a -80°C refrigerator for storage. After collecting the cerebrospinal fluid, the skin can be sutured or sacrificed for follow-up, and then continue to raise the animal.
(2) Standard
Cerebrospinal fluid collected by centrifugation at 2000g for 10 minutes at 4°C for 20 minutes. If the cerebrospinal fluid is light red, it means blood-cerebrospinal fluid and hemolysis: If there is a red deposit at the bottom of the EP tube, it means blood-cerebrospinal fluid, but no hemolysis occurs. Samples containing blood cerebrospinal fluid are considered unqualified.
(3)Result
Among the 20 rats, 18 successfully extracted the cerebrospinal fluid. After centrifugation, the cerebrospinal fluid was clear and transparent without red precipitate. Generally, rats can extract 80-120μl of cerebrospinal fluid, and larger rats can collect 120-140μl of cerebrospinal fluid. The cerebrospinal fluid of two animals was bloody, but 80μl or more of clear cerebrospinal fluid could be obtained after centrifugation.
3 Discussion
Analyzing related components in cerebrospinal fluid is a common method in animal research, because the components in cerebrospinal fluid can indirectly reflect the state of brain tissue. However, due to the limited collection methods and techniques of cerebrospinal fluid, animal research often poses a problem. How to collect enough cerebrospinal fluid while avoiding blood contamination is the key to successful extraction of cerebrospinal fluid. In many previously reported methods of cerebrospinal fluid collection. The appearance of bloody cerebrospinal fluid is a major problem that often plagues researchers. Fast learning of effective cerebrospinal fluid collection methods, especially for beginners, is the key to follow-up treatment. At present, the methods of collecting cerebrospinal fluid reported in Japan and abroad mainly include direct percutaneous puncture of large water tanks, dural puncture of large water tanks under direct vision, and direct visualization of dura puncture. This will be. Based on previous
reported that the author’s research team adjusted the extraction method to establish a more suitable method for beginners. Compared with the method of collecting spinal fluid directly from the skin, the position of the micro-injector is easier to grasp and the operation deviation is smaller. Compared with opening the skin and muscles under direct vision to collect cerebrospinal fluid, simply cutting the skin can prevent damage to the muscles and reduce muscle contamination caused by bleeding. At the same time, if you are a beginner but cannot successfully withdraw the cerebrospinal fluid from the first insertion of the needle due to poor proficiency, the muscle contraction and sealing function will cause the direction or position of the needle to be changed the second or third time. adjustable. In order to avoid the failure to discharge the cerebrospinal fluid under direct vision for the first time, the cerebrospinal fluid is drained very strictly after the needle is removed, and the uncontaminated sample cannot be taken out again. In addition, if the animal needs to continue eating, the method of extracting cerebrospinal fluid through muscle puncture through the medulla oblongata is more invasive than the method of directly opening the skin and muscles. It has major advantages such as small area and rapid recovery of animals. In short, the author studied and established how to open the skin through muscle puncture and puncture the cerebrospinal fluid to extract cerebrospinal fluid. This has the advantages of being simple, fast and efficient. This is an excellent method of collecting cerebrospinal fluid, especially suitable for patients who are not familiar with cerebrospinal fluid.