
RAPD technology is one of the commonly used methods for molecular genetic markers of experimental animals. Due to its advantages of rapidity, simplicity, convenience, economy, and standardization, it has been widely used in animal, plant, and microbial species identification, phylogeny classification, and polymorphism analysis . However, because RAPD technology requires very strict experimental conditions, the results of RAPD reactions are affected by many factors, such as Mg2+, dNTP, template, Taq DNA polymerase (hereinafter referred to as Taq enzyme), reaction time, reaction temperature, and the type of equipment used Wait. The problems that may occur in the experiment and the solutions are introduced as follows:
1. No amplification ①It may be due to the lack of a part of the reactants in some or all of the tubes. Repeat a few reactions to determine whether all the PCR components have been added; ②The PCR inhibitors may be purified together with the DNA to change the concentration of the DNA; ③Add a washing step (such as phenol extraction) in the DNA separation process; ④Dilute the new DNA solution; ⑤If the primer mother solution is invalid, reconstitute the mother solution, use different primers or increase the primer concentration; ⑥Extend the annealing time or reduce the temperature rise The rate between conversion steps; ⑦Increase the concentration of Taq DNA polymerase in each reaction; ⑧Add new components, which need to be autoclaved.
2. The amplification results are poor and the bands are fuzzy and difficult to identify. ①Replace the Taq DNA polymerase buffer; ②Check the primers, use another primer, or label the primer ends, in the case of 6mol/L urea and a gel concentration of 16% (quality Concentration) on polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis; ③Check the activity of Taq DNA polymerase (compared with different batches of enzyme); ④Change the DNA concentration.
3. High-molecular-weight products (>4kb) show a diffuse distribution ①Reduce DNA concentration; ②Reduce Taq DNA polymerase concentration; ③Reduce sample amount; ④May be due to too many cycles, reduce cycle times; ⑤Confirm whether to use Prepare the gel with the correct buffer; ⑥ Electrophoresis at a lower voltage.
4. Band spectrum cannot be repeated Too much or too little DNA will affect the amplified band spectrum. Control the genomic DNA concentration within the range of 10-100ng. When the amount of DNA is too small, the binding efficiency of the "real" target sequence to the primer is low, so primer amplification will produce false bands, which is called primer artifact; DNA; Too much can cause mismatching (pairing of the guide and genomic DNA). Each sample was subjected to two reactions with different DNA concentrations.
5. Factors affecting the repeatability of RAPD patterns RAPD patterns are very sensitive to changes in experimental procedures and conditions. The reliability and repeatability of RAPD in the same laboratory is high, but the comparability of RAPD between different laboratories is poor. Generally, the factors that affect the number, size and intensity of bands include PCR buffer, dNTP and Mg2+ concentration, cycling parameters (annealing temperature, temperature change time, PCR instrument), Taq DNA polymerase source, DNA concentration, and primer concentration. Under normal circumstances: ①The DNA template concentration required for each reaction is 20-80ng; ②The dNTP concentration is 100-200μmoL/L. In the PCR thermal cycling process, when the final concentration of each dNTP is 20-200 μmol/L, the product quantity is high, the specificity and fidelity are good; ③The amount of Taq DNA polymerase concentration in PCR is affected by the reaction volume, enzyme activity, Restricted by factors such as enzyme heat resistance, when the conditions are suitable, 1~1.5U raq DNA polymerase is generally used in every 25μl system. Excessive amount of Taq DNA polymerase will cause non-specific amplification, resulting in a relatively deep background on the gel, which will affect the detection of results, so the amount of Taq DNA polymerase should not be too large; ④The effect of annealing temperature. The annealing temperature is very critical to the specificity of PCR. Too high will cause the primer and template to fail to bind, and too low will cause the primer and template to bind non-specifically and reduce the specificity of amplified fragments. The temperature used for primer annealing depends on the composition, length and concentration of the primer bases. The appropriate annealing temperature should be 5°C lower than the true Tm (melting temperature) value of the primer under PCR conditions.
In view of the problems that may be encountered during the RAPD experiment, combined with our subject, several main influencing factors in the reaction of the Chinese hamster RAPD analysis system were optimized, and the optimal reaction conditions were determined to obtain stable amplification results. Further use RAPD technology to lay the foundation for the genetic research of Chinese hamsters. The specific experiment is as follows:
(1) Materials and methods
1. Materials Chinese hamsters inbred E family and A family, 12 randomly selected as experimental materials. Provided by the Experimental Animal Center of Shanxi Medical University.
2. Reagents Taq enzyme, 10×buffer, MgCl2, dNTP, 30 random primers are all products of Shanghai Sangon Company, and the marker is a product of Dalian Bao Biological Company.
3. Instrument The PCR instrument is PTC-100TM (MJ Company USA), and the electrophoresis instrument is Bio-PAD 500/
200 type, the automatic gel imaging system is GIS 2010 type of Shanghai Tanon Company.
4. Extraction of total genomic DNA Take the Chinese hamster tail tissue and place it in a 1.5ml centrifuge tube and cut it into small pieces. Add 500μl of lysis solution TNES to each tube (TNES composition: 10mmoL/L Tris, pH7.5, 400mmol/L NaCl, 100mmol/L EDTA, 0.6% SDS) 35μl proteinase K (10mg/ml) digestion. Extract with conventional phenol, chloroform, and isopropanol, dissolve it in an appropriate amount of TE buffer, check the DNA concentration, adjust it to 50ng/μl, and store at -20°C for later use.
5. Optimization of RAPD reaction conditions According to relevant RAPD research reports, design Taq enzyme, dNTP, primer
"Substance concentration screening test and Mg2+ concentration, template concentration screening test (Table 4-1, Table 4-2).

6. Annealing temperature and pre-denaturation time design Thermal cycle amplification conditions mainly take annealing temperature and pre-denaturation time as the research objects. According to the data, this experiment designed three procedures: (I) enter the cycle system after pre-denaturation at 94℃ for 5 minutes, denaturation at 94℃ for 30s, annealing at 40℃ for 45s, and extension at 72℃ for 90s. 45 cycles followed by 10 min extension. (II) Denaturation at 94°C for 2min, annealing at 38°C for 1min, extension at 72°C for 2min, 45 cycles. (Ⅲ) After pre-denaturation at 94°C for 3min, enter the circulation system, denaturation at 94°C for 30s, annealing at 36°C for 50s, extension at 72°C for 1min, 40 cycles followed by 7min extension.
7. Electrophoresis analysis of amplified product Take 8μl of amplified product and analyze it by electrophoresis on 1.4% agarose gel containing 0.5μg/ml EB staining solution.
(two) result
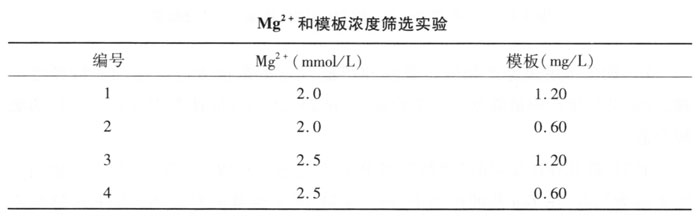
1. Taq enzyme, dNTP, primer concentration screening According to the experimental design, PCR amplification and electrophoresis detection are carried out. Some results are shown in Figure 4-1. Taq enzymes are divided into 3 groups: the first group is 0.04U/μl, the second group is 0.08U/μl, and the third group is 0.06U/μl. Results The 0.06U/μl amplified band in the second group was clear and stable, the corresponding dNTP was 0.2mmol/L, and the primer was 0.2μmol/L, which was the best combination. Lanes 7, 8, 9 in Figure 4-1. The results show that: Taq enzyme, dNTP, primer concentration all have an effect on RAPD.
The concentration of Taq enzyme determines the specificity and yield of the product. Too high a concentration of Taq enzyme will increase non-specific products, and too low a concentration will reduce the amount of product. This experiment believes that it is more appropriate to add 1.5U enzyme to the 25μl reaction system.
dNTP is the "raw material" of the RAPD reaction. When the PCR reaction enters the amplification and extension stage, the 3'end of the primer is used as the starting point. Under the action of Taq enzyme, the dNTP is extended and bound according to the base pairing rule with single-stranded DNA. , Resulting in different fragments. Too high dNTP concentration will cause false infiltration, increase base mismatches, and increase non-specific products and increase non-specific bands in the RAPD band; too low dNTP concentration will result in too low RAPD yield, which is manifested as a change in the bright band in the RAPD band The strong and weak bands disappear, so too low or too high will affect the accuracy of the amplification results. In this experiment, we performed RAPD at dNTP concentrations of 150, 200, and 250 μmol/L, and found that the amplification results were better when the dNTP concentration was 200 μmol/L. The primer concentration also needs an appropriate amount, and the reaction system contains 0.2μmoL/L primer. Since the RAPD reaction uses a single random primer, the use of high-concentration primers in the reaction system is more conducive to the chance of primer and template mismatch, but the primer concentration should not be too high, otherwise non-specific products will be produced.
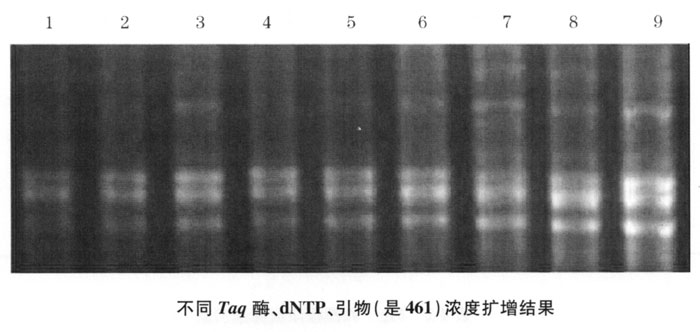
2. Screening of Mg2+ concentration and template DNA concentration Through the Mg2+ and template DNA concentration screening experiment, PCR amplification, electrophoresis results are shown in Figure 4-2: Lanes 1, 2 are Mg2+ concentration 2.0mmoL/L, template DNA concentration 1.20mg/L, Lanes 3 and 4 are Mg2+ concentration 2.0mmoL/L, template DNA concentration 0.60mg/L, lanes 5 and 6 are Mg2+ concentration 2.5mmoL/L, template DNA concentration 1.20mg/L, lanes 7, 8 are Mg2+ concentration 2.5mmoL/ L. The template DNA concentration is 0.60 mg/L. The effects of lanes 3 and 4 are better.
From this study and related data, it is shown that too high or too low Mg2+ concentration will affect the amplification results, and Mg2+ concentration indirectly affects RAPD amplification mainly by affecting the activity of Taq enzyme. Mg2+ is the activator of Taq enzyme. Too low Mg2+ concentration does not have enough activating effect on Taq enzyme, and too high concentration will inhibit the activity of the enzyme. In addition to directly affecting the specificity and efficiency of PCR, Mg2+ is also conducive to the combination of primers and templates and increases the stability of the combination of primers and templates. This is more important for RAPD reactions using non-specific primers. However, the Mg2+ concentration shown in the reaction system is not necessarily the free Mg2+ concentration participating in the reaction, because the concentration, purity, primers, and dNTPs of the DNA template in the reaction system will all affect the Mg2+ concentration. Therefore, when optimizing the optimal concentration of Mg2+, several concentration gradients should be set to accurately the optimal concentration. After screening in this experiment, it is believed that the amplification result is better when the Mg2+ concentration is 2.0mmoL/L.
Genomic DNA requires high purity and good quality, which is a prerequisite to ensure good amplification effect and good repeatability. If too much phenol, chloroform, ethanol, protein, etc. remain in the DNA preparation process, it will affect RAPD, because these substances directly affect the activity of Taq enzyme; in addition, the author also found that the degraded template DNA has an effect on the template concentration. It is very sensitive, that is, different concentrations will have different amplification patterns, and the extent of its influence is still under investigation. Therefore, the RAPD technology may be limited when studying materials that have DNA degradation due to various reasons.
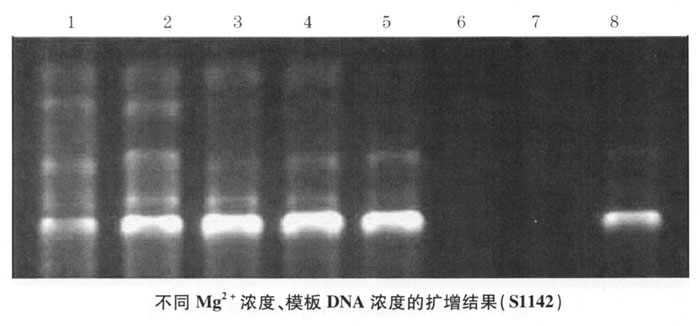
3. The selection of thermal cycling conditions is amplified according to the three programs designed in the annealing temperature and pre-denaturation time study. The electrophoresis results are shown in Figure 4-3. Lanes 1, 2, and 3 are the results of the amplification program I, 4, 5 , 6 are the results of the II amplification program, 7, 8, and 9 are the results of the III amplification program. Ⅲ The results of the amplification program are better: that is, it enters the circulation system after pre-denaturation at 94°C for 3 minutes, denaturation at 94°C for 30 seconds, annealing at 36°C for 50 seconds, extension at 72°C for 1 minute, and 7 minutes extension after 40 cycles. The amplified product was finally stored at 4°C.
In the RAPD system, different template DNA and different primers have different optimal annealing temperatures. In the experiment, we used primers to react with the template DNA of Chinese hamsters, and performed RAPD at annealing temperatures of 36°C, 38°C, and 40°C, and found negative results at 40°C. Calculate the annealing temperature based on the G+C content of the primers used, and decide that the temperature does not exceed 40°C. And according to literature reports, the negative rate of RAPD increases gradually with the increase of annealing temperature. Under the annealing condition of 45℃, the negative rate is not only higher, but the RAPD band becomes weaker, indicating that with the increase of annealing temperature, primers and The specificity of template binding is enhanced, and the probability of binding is reduced. Conversely, the specificity of primer and template binding decreases and the probability of binding increases. Considering that it is necessary to avoid negative results as much as possible, but also to enhance the specificity of the results, we think that the annealing temperature is 36℃.
The number of RAPD cycles directly affects the amount of amplified product and the specificity of the results. The number of cycles is small, and the amount of product is small; if there are too many cycles, non-specific products will be produced. Because the PCR reaction reaches a certain level, a platform effect will occur. Too many cycles will increase the number and complexity of non-specific products. In this experiment, 35-40 cycles are sufficient.
According to the above experiments, it is determined that the best combination of Chinese hamster RAPD reaction system and temperature cycling parameters is: 10×buffer 2.5μl, dNTP 0.20 mmol/L, Mg2+ 2.0mmol/L, primer 0.12μmol/L in a 25μl reaction system , Taq enzyme 1.5U, template DNA 15ng, amplification program is 94°C pre-denaturation for 3min, then enter the cycle system, 94°C denaturation for 30s, 36°C annealing for 50s, 72°C extension for 1min, 40 cycles followed by 7min extension.
(3) Discussion
The basic reaction procedure of RAPD is PCR reaction. Therefore, only by studying the optimal reaction conditions can an ideal RAPD profile be obtained. There are many factors affecting RAPD-PCR. In addition to the factors involved in this experiment, the following aspects should be noted:
1. Blank control should be set up During the RAPD experiment process, it is necessary to set up a blank control without template for each amplification reaction, so as to eliminate the contamination caused by air, experimental utensils or reagents and operators during the experimental operation. A small amount of bands in the blank is also very common. The reason is that the Taq enzyme comes from the thermophilic bacteria, which is prepared and purified by bioengineering. In this process, there is a small amount of DNA of the engineered bacteria, so that the reaction sample template is not added. Amplification also occurs below, and the band type statistics should be excluded when such bands appear in each sample.
2. It is best to use the same batch of reagents from the same manufacturer. In this experiment, it was found that Taq enzymes from different sources and different batches have different activities. In RAPD amplification, use the same Taq enzyme as much as possible to avoid replacing it in the middle. important. Subtle differences in the composition of the reaction buffer produced by different manufacturers, even if the buffer produced by the same manufacturer, if the Mg2+ and Taq enzymes used do not match it, sometimes affects RAPD.
3. The quality of the experimenter The difference in the quality of the experimenter also has an impact on the reaction, but as long as the conditions are stable, a rigorous attitude is cultivated in the operation, and sufficient attention is paid to the influencing factors. The result is repeatable. The RAPD technology itself is stable.