
A large amount of data proves that intense stress, especially long-term
chronic stress, seriously affects human physical and mental health, and leads to
abnormal emotions and behaviors. This experiment establishes a psychological
stress model on the basis of relevant literature, observes its influence on the
general behavior of rats, and conducts a preliminary discussion on the role of
Gln in the body's stress response.
Materials and Methods
1. Animals and grouping conditions: 30 Wistar rats in the growth period,
half male and half, weighing 100 ± 20 g, were randomly divided into three
groups: group I was the control group, group II was the stress group, and group
III was the stress + Gln group. Groups I and II were fed with ordinary feed, and
group III was fed with feed supplemented with 2% Gln. Animals in each group were
raised in single cages in stainless steel cages, with free access to food and
water, and weighed once a week.
2. Establishment of the stress model: After the animals were kept for 2
weeks, light and plantar electric shocks were used as conditioned and
unconditional stimuli to establish stress models in group II and group III
animals. The experimental equipment and methods are as follows: The size of the
experiment box is 30 × 25 × 18cm, the bottom of the box is composed of stainless
steel rods with a diameter of 0.4cm and an interval of 0.5cm, which can be
energized, and a flashlight is installed on the top of the box. During the
experiment, the rats were put into the box to adapt to 1min and then given
intermittent and irregular photoelectric stimulation (electric shock parameters:
40~60V, AC, stimulation every 5~15 seconds for 0.5~5 seconds), lasting 5min,
repeat the procedure On the 6th day, only light stimulation was given on the 7th
day without electric shock.
3. Observation index and measurement method
1. Spontaneous and exploratory behavior: After the animal stress period is
over, the open field behavior experiment method is used to observe the
spontaneous and exploratory behavior of the animal in the experiment box. The
open field experiment box is provided by Shanghai Xinruan Information Technology
Co., Ltd. The experimental device and method are as follows: The size of the
experiment box is 100×100×50cm, and the bottom plate is automatically divided
into 25 squares with SuperMaze software. During the experiment, the animal was
placed in the center grid, and its activities within 5 min were recorded,
including the staying time in the center grid, the number of grids passing, the
number of standing upright, and the number of modifications.
2. Darkness avoidance reaction: Darkness avoidance experiment box is
provided by Shanghai Xinruan Information Technology Co., Ltd. It is divided into
large and small rooms, the small room is 25×15×18cm, the light is on and the
bottom of the box has no electricity, and the large room is 25×30 × 18cm, dark
and the bottom of the box is energized. During the experiment, place the animal
on the side where the light is lit, and observe the reaction of the animal
within 5 min to avoid darkness.
3. The content of glucocorticoid and adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) in
plasma: blood was taken after the animal was decapitated, anticoagulated with 1%
heparin, centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 15 min, and the supernatant was taken. The
use of Depu Biotechnology is limited. The radioimmunoassay kit produced by the
company measures glucocorticoids and A CTH.
4. Statistical analysis: The experimental results are expressed as x ± s or
the median (M), the open field behavior index, the dark avoidance latency and
the escape time are tested by the rank sum test, the response rate is tested by
ς2, and the rest are compared by the t test. .
Result
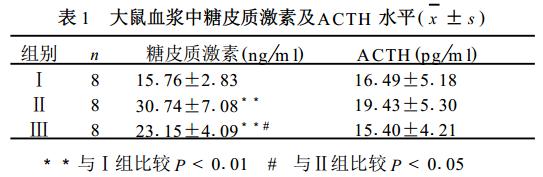
1. Plasma glucocorticoid and A CTH levels: Table 1 shows that the plasma
glucocorticoids of rats in groups II and III are significantly higher than those
in group I (P<01 01), indicating that these two groups of rats are under
stress status. However, group III was significantly lower than group II (P
<01 05), suggesting that supplementation of Gln can reduce the body's stress
response. There was no significant difference in plasma A CTH levels among the
three groups.
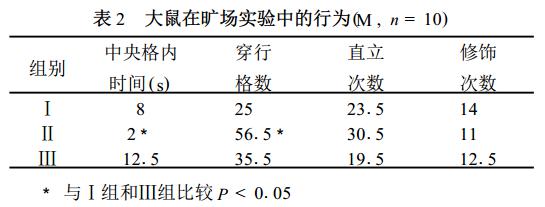
2. Open field behavior
It can be seen from Table 2 that compared with groups I and III, the staying time of the rats in group II in the central grid was significantly shorter, and the number of crossing grids increased significantly (P <01 05), and there was no significant difference in the number of upright and modification times. , Indicating that stress increases spontaneous activities of rats, and supplementation of Gln can reduce the activities of stressed rats.
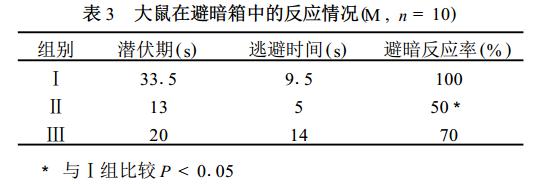
3. Darkness avoidance reaction: The dark avoidance reaction rate of rats in group II is only 50%, which is significantly lower than that of group I (P <01 05), and group III is between group I and group II, but not with both Significant difference (Table 3). Although the incubation period and escape time of rats in group II have a decreasing trend compared with groups I and III, the difference is not significant.
Discuss
1. The establishment of a rat psychological stress model: Psychological stress refers to the process of changes in the psychological and physiological functions of the body when the body perceives the threat of the stressor through cognition and evaluation. Regarding the psychological stress model, most of the literature reports are restraints and electric shocks, but they inevitably contain physical stress components. This experiment uses a relatively "pure" psychological stress model reported in the literature recently, that is, lighting and electric shock are used as conditioned and unconditioned stimuli to establish conditioned reflex. When only the lights appear, the animals will still be nervous and fearful. At this time, the physical stimulation has been reduced to a minimum, so the main psychological stress components are at work. The results of this experiment showed that glucocorticoids in the plasma of stressed rats increased significantly, indicating that the stress model is feasible.
2. The effect of stress on the behavior of rats and the effect of Gln: It is generally believed that stress causes the activity of the hypothalamic pituitary adrenal axis to increase, which acts through glucocorticoids, which leads to a series of changes in metabolism and function. It can be seen from the results of this experiment that stress has a certain impact on the behavior of rats. In the open field behavior experiment, the staying time of the stressed rats in the central grid was shortened and the number of walking grids increased, indicating that the activity of the rats increased, which may be an anxiety manifestation in the early stage of stress. The open field experiment mainly reflects the spontaneous behavior and exploratory activities of the animals, and the number of activities indicates to a certain extent the state of excitement or inhibition of CNS. Studies have shown that the behavioral activities of animals in the acute stress period increase, while the chronic stress period decreases. It is speculated that the stressed rats in this experiment may still be in the acute period.
Avoiding darkness is a habit of rodents. In this experiment, 50% of the rats in the stress group did not enter the dark room within 5 minutes, and those who entered the dark room had shorter latency and escape time, which reflected the abnormal behavior of the stressed rats; at the same time, it also showed that the stress The ambivalence of depression, tension and anxiety in rats indicates the complexity of animal behavior. This complexity may be related to the stimulus that caused the stress state.
In recent years, people have tried to find ways to reduce stress damage from nutrition and food ways and made some progress. If there is information, vitamins with antioxidant effects such as Vitamin C, Vitamin E, Beta-carotene and some vegetables and fruits may have potential anti-stress effects. It can be seen from the results of this experiment that supplementation of Gln reduces the spontaneous activity of stressed rats, which may have a certain effect on improving the mood and behavior abnormalities of rats caused by excessive excitement in the early stage of stress. It has been reported in the literature that supplementing clinical patients with Gln can improve their mood while promoting their recovery, which is basically consistent with the results of this experiment.